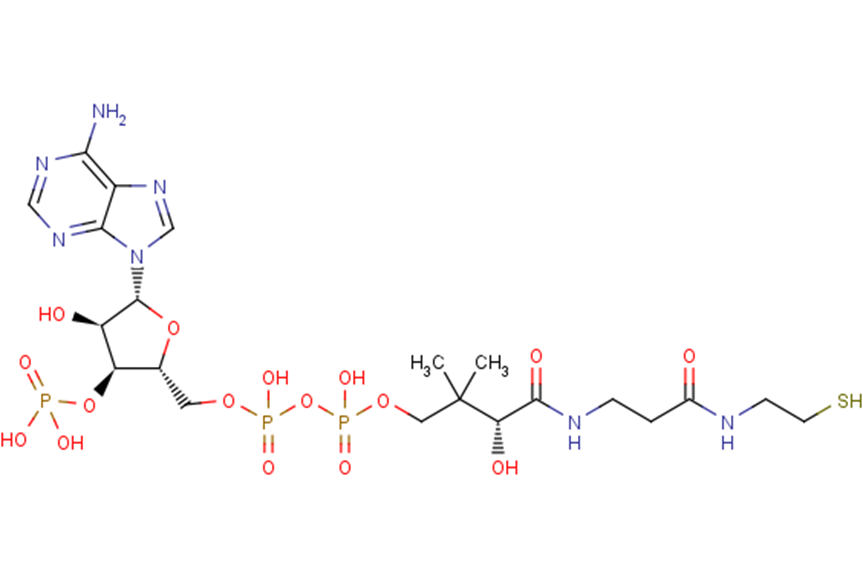
Coenzyme A
CAS No. 85-61-0
Coenzyme A( —— )
Catalog No. M22129 CAS No. 85-61-0
Coenzyme A is an obligatory cofactor in all living cells synthesized from pantothenate (Vitamin B5), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and cysteine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 32 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 42 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 68 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 101 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 149 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 221 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 374 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCoenzyme A
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCoenzyme A is an obligatory cofactor in all living cells synthesized from pantothenate (Vitamin B5), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and cysteine.
-
DescriptionCoenzyme A is an obligatory cofactor in all living cells synthesized from pantothenate (Vitamin B5), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and cysteine.Covalent binding of Coenzyme A to Peroxiredoxin 5 (Prdx5) results in complete inhibition of its peroxidase activity, which is reversed by reduction with DTT. Many human pathologies, including cancer, diabetes, and neurodegeneration, have been associated with abnormal biosynthesis and homeostasis of CoA and its derivatives.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research AreaCardiovascular system
-
IndicationHyperlipoproteinemia
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number85-61-0
-
Formula Weight767.53
-
Molecular FormulaC21H36N7O16P3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 125 mg/mL (162.86 mM)
-
SMILESCC(C)(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)(O)=O)n1cnc2c(N)ncnc12)[C@@H](O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCS
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Bakovi? J, et al. A key metabolic integrator, coenzyme A, modulates the activity of peroxiredoxin 5 via covalent modification. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Aug 2.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Vitamin A
Retinol, also known as Vitamin A1, has pleiotropic functions including vison, immunity, hematopoiesis, reproduction, cell differentiation/growth, and development.
-
Cyclic N-Acetyl-D-ma...
N-Acetylmannosamine is a monosaccharide that is used as a precursor in the chemical or enzymatic synthesis of the neuraminic acids found in glycolipids and glycoproteins.
-
2'-Deoxycytidine-5'-...
2′-Deoxycytidine 5′-diphosphate (dCDP) is used as a substrate of CDP (nucleoside diphosphate) kinase (2.7.4.6) for the production of dCTP to support DNA biosynthesis and reverse transcription.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


